Understanding Om Heart Blockage: A Comprehensive Guide
Om heart blockage, also known as atrioventricular blockage, is a condition that affects the electrical signals in your heart. This guide will delve into the details of this condition, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what om heart blockage is and how it can be managed.
What is Om Heart Blockage?
Om heart blockage occurs when the electrical signals that coordinate the heartbeat are disrupted. These signals travel from the upper chambers (atria) to the lower chambers (ventricles) through a pathway called the atrioventricular (AV) node. When this node is damaged or not functioning properly, it can lead to an om heart blockage.
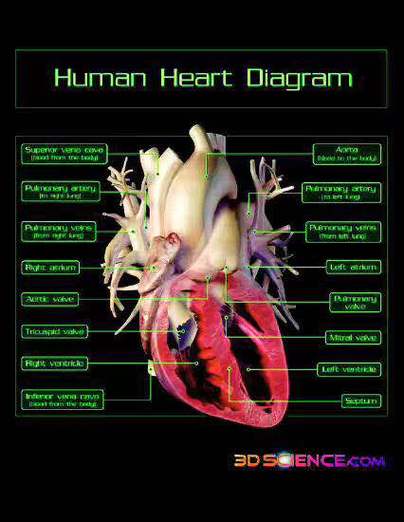
Types of Om Heart Blockage
There are several types of om heart blockage, each with varying degrees of severity:
| Type | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| First-degree blockage | Mild | There is a delay in the electrical signal, but the heart still beats normally. |
| Second-degree blockage | More severe | Some electrical signals are blocked, causing the heart to beat irregularly. |
| Third-degree blockage | Severe | All electrical signals are blocked, and the heart beats irregularly or stops. |
Causes of Om Heart Blockage
Om heart blockage can be caused by various factors, including:
- Age: As you get older, the risk of developing an om heart blockage increases.
- Heart conditions: Conditions such as myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure can lead to om heart blockage.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as those used to treat heart rhythm disorders, can cause om heart blockage.
- Structural heart defects: Congenital heart defects can increase the risk of om heart blockage.
- Infections: Viral infections, such as myocarditis, can cause damage to the heart’s electrical system.
Symptoms of Om Heart Blockage
The symptoms of om heart blockage can vary depending on the type and severity of the blockage. Common symptoms include:
- Palpitations: A sensation of irregular or rapid heartbeat.
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Cardiac arrest
In some cases, om heart blockage may not cause any symptoms, especially in the early stages.

Diagnosis of Om Heart Blockage
Diagnosing om heart blockage typically involves the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of your heart and can detect om heart blockage.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to create images of your heart, helping to assess its structure and function.
- Holter monitor: This device records your heart’s electrical activity over a period of time, usually 24 to 48 hours.
- Event recorder: This device is worn for a longer period, typically weeks or months, to capture any irregular heartbeats.
Treatment of Om Heart Blockage
The treatment for om heart blockage depends on the type and severity of the blockage, as well as your overall health. Treatment options include:
- Medications: Medications such as beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers can help control heart rate and rhythm.
- Cardiac pacemaker: A pacemaker is a small device that sends electrical impulses to the heart to maintain a normal heartbeat.
- Defibrillator: A defibrillator is a device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal heartbeat.
- Heart transplant: In some cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.




